Cabinetry, Plywood, Uncategorized
Nesting Parts Explained in CNC Router Applications
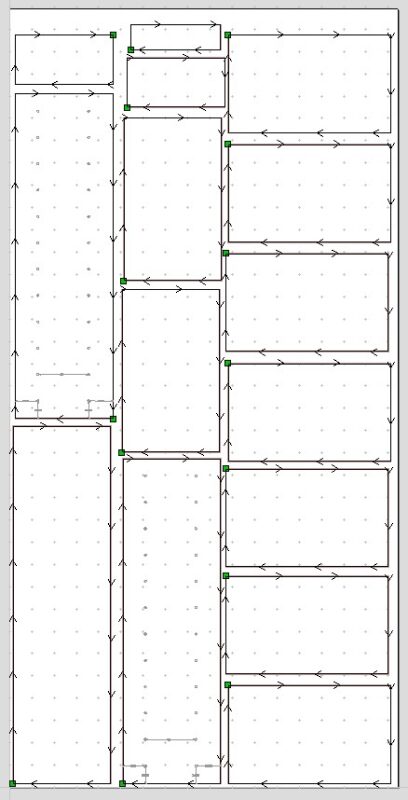
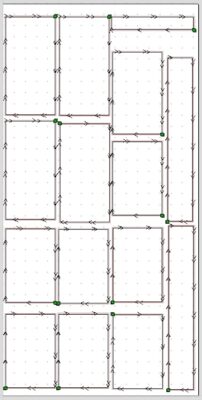
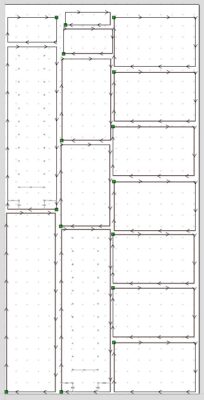
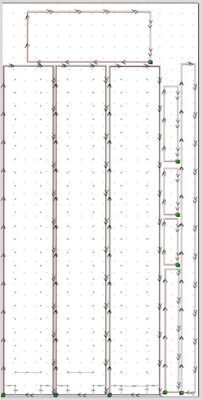
Nesting is a strategy used in computer numerical control (CNC) router cutting to maximize the use of material by arranging parts in the most efficient way possible on a sheet of material. It involves placing the parts in such a way that they use as little material as possible and minimize waste. This can be done manually or using specialized software such as Mozaik for cabinetry or VCarve Pro. The software analyzes the shapes of the parts and arranges them in the most optimal way to reduce the amount of material used and the number of scrap pieces generated. This results in cost savings and increased efficiency in the production process.
In more detail, Nesting in CNC router cutting involves taking a set of individual parts or shapes and arranging them in the most space-efficient manner on a flat sheet of material, such as wood, metal, plastic, etc. The goal is to maximize the utilization of the available material, reduce waste, and increase efficiency.
During the nesting process, the CNC software takes into account factors such as the shape of the parts, their size and orientation, and the cutting tool used. Based on this information, it generates a nesting layout that minimizes the amount of material used, while also reducing the number of scrap pieces generated. IF your pieces have a grain pattern, the software will take that into account and keep things from rotating inconsistently.
The benefits of nesting as a strategy in CNC router cutting are significant. By reducing waste, companies save on material costs and minimize their environmental impact. Additionally, by using less material and reducing the number of scrap pieces, companies also reduce their storage and disposal costs. And by maximizing the use of material, companies can increase their production efficiency, as well as their competitiveness by providing customers with a more cost-effective solution.